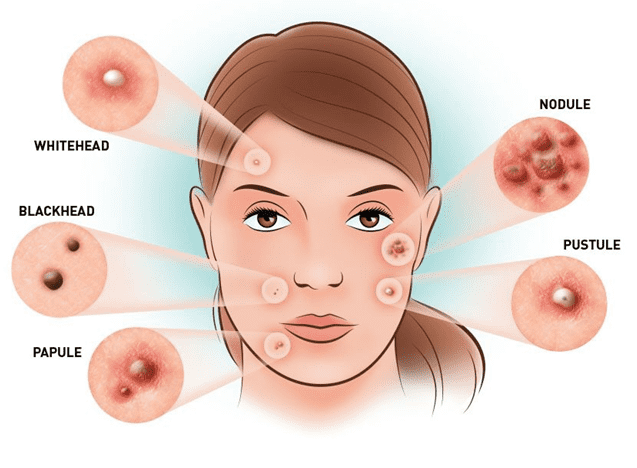
Acne is a common skin condition that causes pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, and sometimes cysts or nodules on your face and other parts of your body. Acne can affect anyone at any age, but it is most common among teenagers and young adults. Acne can cause physical and emotional distress and may lead to scarring if left untreated. In this blog post, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment of acne, as well as some tips on how to prevent and cope with it.
What causes acne?
Acne is caused by the clogging of hair follicles under the skin with oil (sebum) and dead skin cells. When the clogged follicle becomes infected with bacteria, it forms a pimple. Acne can be influenced by various factors, such as:
• Hormones: Hormonal changes during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause can increase the production of sebum and cause acne. Some hormonal disorders, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can also cause acne.
• Genetics: Acne can run in families and you may be more prone to develop it if your parents or siblings had it.
• Medications: Some medications can cause acne as a side effect or interact with your skin’s oil production. Some of the common medications that can cause acne are antibiotics, antihistamines, anticonvulsants, immunosuppressants, chemotherapy drugs, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
• Diet: Some foods may trigger or worsen acne in some people. These include foods that are high in sugar, dairy products, chocolate, and spicy foods.
• Stress: Stress can affect your hormones and immune system and make your acne worse.
• Environment: Exposure to heat, humidity, pollution, or certain chemicals can irritate your skin and clog your pores.
What are the symptoms of acne?
The main symptom of acne is having pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, or cysts on your skin. These can vary in size, number, and severity depending on the type of acne you have. The common types of acne are:
• Comedonal acne: This type of acne causes blackheads and whiteheads on your forehead, nose, and chin. These are clogged pores that have a black or white top.
• Inflammatory acne: This type of acne causes red, swollen, and painful pimples on your face, chest, back, and shoulders. These are infected pores that have a yellow or white pus-filled top.
• Nodular or cystic acne: This type of acne causes large, hard, and painful lumps under your skin that may leave scars. These are deep infections that affect the deeper layers of your skin.
How is acne diagnosed?
Acne is usually diagnosed based on the appearance of your skin and medical history. Your healthcare provider may ask you about your symptoms when they started, how they affect you, what treatments you have tried, and what medications you are taking. In some cases, you may need additional tests to rule out other conditions that can cause similar symptoms or to identify the cause of your acne. These tests may include:
• Blood tests: To check for signs of infection, inflammation, diabetes, thyroid problems or hormonal imbalances.
• Urine tests: To check for signs of diabetes or kidney problems.
• Stool tests: To check for signs of intestinal infections or parasites.
• Chest X-rays: To check for signs of lung infections or pneumonia.
• CT scans or MRI scans: To check for signs of brain infections or tumors.
How is acne treated?
The treatment of acne depends on the type and severity of your acne and your personal preferences. The main goals of treatment are to clear your skin from pimples, prevent new ones from forming, reduce inflammation and scarring and improve your quality of life. Some of the common treatments for acne are:
• Topical medications: These are creams, gels or lotions that you apply directly to your skin to treat mild to moderate acne. They work by killing bacteria, reducing inflammation, unclogging pores or preventing new pimples from forming. Some of the common topical medications for acne are benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, retinoids (such as tretinoin or adapalene), antibiotics (such as clindamycin or erythromycin), azelaic acid or dapsone.
• Oral medications: These are pills that you take by mouth to treat moderate to severe acne. They work by killing bacteria, reducing inflammation, regulating hormones or preventing new pimples from forming. Some of the common oral medications for acne are antibiotics (such as doxycycline or minocycline), isotretinoin (a powerful retinoid that requires close monitoring), oral contraceptives (for women who have hormonal acne), spironolactone (an anti-androgen that blocks the effect of male hormones on the skin) or corticosteroids (for severe inflammatory acne).
• Procedures: These are treatments that involve physical removal or destruction of pimples or scars by a healthcare provider. They work by extracting clogged pores, peeling off dead skin cells, reducing inflammation, or stimulating new skin growth. Some of the common procedures for acne are extraction (using special tools to clear blackheads and whiteheads), chemical peel (applying a chemical solution to exfoliate the skin), phototherapy (using light to kill bacteria or reduce inflammation), laser therapy (using a laser beam to vaporize pimples or scars) or surgery (cutting out cysts or nodules).
How can acne be prevented?
Some tips to prevent acne include:
• Using a light detergent and warm water, wash your face twice a day. Scrubbing or using strong products that might irritate your skin should be avoided.
• Moisturizing your skin with a non-comedogenic product that does not clog your pores.
• Protecting your skin from the sun with a sunscreen that does not clog your pores.
• Avoiding touching, picking or popping your pimples as this can spread bacteria and cause scarring.
• Changing your pillowcase regularly as it can accumulate oil and dirt from your hair and face.
• Avoiding wearing tight-fitting clothes or hats that can trap sweat and bacteria on your skin.
• Eating a nutritious diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean meats. Avoid foods that trigger or worsen your acne such as sugar, dairy products, chocolate, or spicy foods.
• Drinking plenty of water to keep your skin hydrated and flush out toxins from your body.
• Stress management through relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, or breathing exercises.
Conclusion
Acne is a common skin condition that causes pimples blackheads whiteheads cysts on your face and other parts of your body Acne can affect anyone at any age but it is most common among teenagers and young adults Acne can cause physical and emotional distress and may lead to scarring if left untreated Acne is caused by the clogging of hair follicles under the skin with oil sebum dead skin cells Acne can be influenced by various factors such as hormones genetics medications diet stress environment Acne can be diagnosed by the appearance of your skin medical history In some cases additional tests may be needed Acne can be treated by topical medications oral medications procedures The main goals of treatment are to clear your skin prevent new pimples reduce inflammation scarring improve quality life Acne can be prevented by washing face moisturizing protecting sun avoiding touching changing pillowcase avoiding tight clothes eating healthy drinking water managing stress.