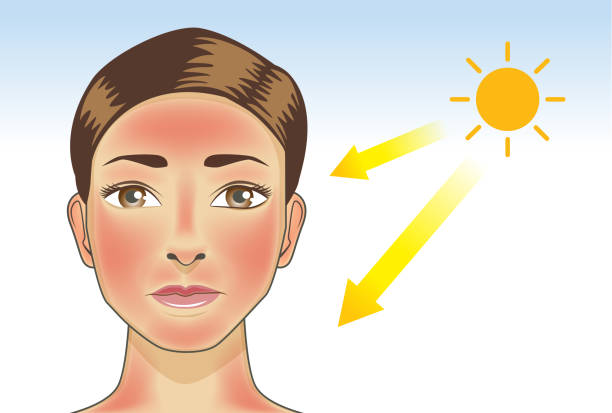
Redness is a common skin condition that can affect any part of the body or the whole body. Redness can be caused by various factors, such as sunburn, irritation, allergy, infection, or disease. In this blog post, we will explore some of the most common causes, symptoms, and treatment options for redness.
What is redness?
Redness, also known as erythema or flushing, is a term that describes abnormal redness or discoloration of the skin. Redness can result from increased blood flow to the skin surface due to inflammation, dilation of blood vessels, or leakage of blood into the tissues.
Redness can be classified into two types:
• Transient redness: This refers to redness that lasts for a short time and fades away. Transient redness can be caused by temporary factors such as emotions, exercise, heat, cold, alcohol, or spicy foods.
• Persistent redness: This refers to redness that lasts for a long time and does not fade away. Persistent redness can be caused by chronic factors such as skin disorders, systemic diseases, or medications.
What are the symptoms of redness?
The main symptom of redness is the change in color or appearance of the affected skin area. Other symptoms may include:
• Warmth or heat in the skin.
• Skin tingling or burning feelings.
• Itching or dryness of the skin.
• Swelling or thickening of the skin.
• Bumps, blisters, rash, or scales on the skin.
The severity and duration of redness may vary depending on the cause and location of the redness. Some redness may be mild and harmless while some may be severe and distressing.
What causes redness?
There are many possible causes of redness, but some of the most common ones include:
• Sunburn: Sunburn is a type of skin damage caused by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun or artificial sources. Sunburn can cause redness, pain, peeling, and blistering of the skin. Sunburn can also increase the risk of skin cancer and premature aging of the skin.
• Irritation: Irritation is a type of skin reaction that occurs after contact with a substance that bothers the skin. Common irritants include soaps, detergents, chemicals, cosmetics, perfumes, plants, or metals. Irritation can cause redness, rash, itching, or burning of the skin.
• Allergy: Allergy is a type of immune reaction that occurs after contact with a substance that triggers an abnormal response in the body. Common allergens include foods, drugs, insect stings, pollen, dust mites, animal dander, mold spores, latex, or cosmetics. Allergy can cause redness, hives, swelling, itching, or anaphylaxis (a severe allergic reaction that can be life-threatening).
• Infection: Infection is a condition that occurs when microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, or parasites invade and multiply in the body. Infection can affect any part of the body and cause fever, redness, warmth, pus, or abscess. Some common infections that cause redness include fungal infections (such as athlete’s foot or ringworm), bacterial infections (such as impetigo or cellulitis), viral infections (such as chickenpox or herpes), or parasitic infections (such as scabies or lice).
• Disease: Disease is a condition that affects the normal functioning of the body or its organs. Disease can cause redness by affecting the blood vessels, nerves, hormones, or immune system that regulate the blood flow and sensation in the skin. Some common diseases
that cause redness include: Rosacea: This is a chronic skin disorder that causes persistent redness and flushing of the face. Rosacea can also cause pimples, visible blood vessels, eye irritation, and thickening of the nose.
Lupus: This is a chronic autoimmune disease that causes inflammation and damage to various organs and tissues. Lupus can cause a butterfly-shaped rash across the nose and cheeks, as well as other symptoms such as joint pain, fatigue, fever, and hair loss. Scarlet fever: This is a bacterial infection that causes a bright red rash that covers most of the body. Scarlet fever can also cause a sore throat, fever, headache, and a strawberry-like tongue. Psoriasis: This is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that causes thickened, red, scaly patches on the skin. Psoriasis can also affect the nails and joints.
Eczema: This is a group of inflammatory skin conditions that cause dry, red, itchy patches on the skin. Eczema can also cause blisters, cracks, and bleeding.
How are redness diagnosed?
To diagnose redness, a healthcare provider will usually ask about the history and characteristics of the redness. They may ask questions such as:
When did the redness start?
Where is the redness located?
How severe is the redness?
What makes the redness better or worse?
Do you have any other symptoms?
Do you have any medical conditions?
Do you take any medications?
Do you have any allergies?
Have you had any recent exposures to irritants or allergens?
Then, your healthcare provider will perform a physical examination to look for signs of injury, infection, inflammation, or disease in the affected area. Depending on the suspected cause of the redness, your healthcare provider may order some tests to confirm the diagnosis or rule out other causes.
These tests may include:
Skin scrapings: These are samples of skin cells taken from the affected area and examined under a microscope for signs of infection or disease.
Skin biopsies: These are small pieces of skin tissue taken from the affected area and sent to a laboratory for analysis.
Blood tests: These are tests that measure levels of blood cells, electrolytes, enzymes, hormones, or other substances that may indicate infection, disease, or allergy.
Allergy tests: These are tests that expose your skin to small amounts of potential allergens and observe your reaction to identify your triggers.
How are redness treated?
The treatment of redness depends on the cause and severity of the redness. Some general treatment options include:
Self-care: This involves taking steps to soothe and protect your skin and prevent further irritation or infection. Some self-care measures include: Applying a cold compress to the area to reduce inflammation and numb nerve endings. Using moisturizers to hydrate and repair dry or damaged skin. Avoiding scratching or rubbing the area to prevent damage and infection of the skin. Wearing sunscreen to protect your skin from sun damage and prevent further redness. Avoiding exposure to potential irritants or allergens such as soaps, detergents, chemicals, cosmetics, perfumes, plants, or metals.
Medications: These are drugs that help treat infection, inflammation, allergy, disease, or organ failure that may cause or worsen redness. Some medications include: Antibiotics to to treat bacterial infections. Antifungals to treat fungal infections. Antivirals to treat viral infections. Anti-inflammatories to reduce inflammation and pain. Antihistamines to relieve allergy symptoms such as itching and sneezing. Vasoconstrictors to narrow blood vessels and reduce blood flow to the affected area. Immunosuppressants to suppress immune system activity and reduce inflammation in autoimmune diseases. Biologics to target specific molecules involved in inflammatory processes in chronic diseases.
Procedures: These are treatments that involve using devices, instruments, or techniques to remove, destroy, or modify the affected tissue. Some procedures include: Laser therapy: This involves using focused beams of light energy to vaporize, cut, or coagulate tissue. Laser therapy can help treat conditions such as rosacea, psoriasis, eczema, and scars.
Cryotherapy: This involves using extremely cold temperatures to freeze and destroy tissue. Cryotherapy can help treat conditions such as warts, skin tags, and actinic keratosis. Electrocautery: This involves using electric current to burn and seal tissue. Electrocautery can help treat conditions such as warts, skin tags, and moles. Surgery: This involves using surgical tools to remove tissue. Surgery can help treat conditions such as tumors, cysts, and abscesses.