Urinary Tract Infections, commonly known as UTIs, are among the most frequently occurring bacterial infections, especially in women. While they are typically not life-threatening, they can cause significant discomfort and lead to more serious health problems if not treated promptly.
Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and knowing how to prevent UTIs can go a long way in maintaining urinary health and avoiding unnecessary complications.
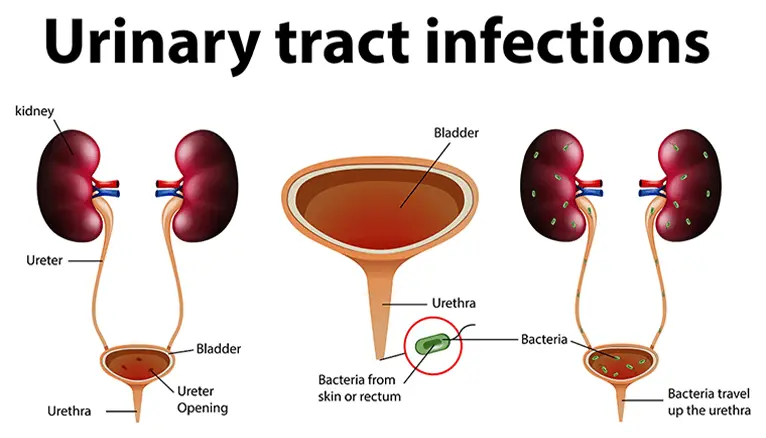
A UTI is an infection that occurs anywhere in the urinary system, which includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Most infections involve the lower urinary tract — the bladder and the urethra. However, more severe cases can affect the kidneys and may require urgent medical attention.
Types of UTIs
UTIs are generally classified based on where they occur in the urinary tract:
- Cystitis (Bladder infection): Most common type, causing inflammation of the bladder.
- Urethritis (Urethra infection): Involves the tube that carries urine out of the body.
- Pyelonephritis (Kidney infection): A more serious infection that can lead to permanent kidney damage if left untreated.
What Causes UTIs?
UTIs are typically caused by bacteria, most often Escherichia coli (E. coli), which naturally lives in the intestines. These bacteria can enter the urinary tract through the urethra and begin to multiply in the bladder.
Common causes and risk factors include:
- Poor hygiene practices
- Sexual activity
- Urinary retention (incomplete bladder emptying)
- Use of catheters
- Menopause (due to hormonal changes)
- Weakened immune system
- Anatomical abnormalities in the urinary tract
Symptoms of a UTI
Symptoms can vary depending on the part of the urinary tract affected, but common signs include:
- A strong, persistent urge to urinate
- A burning sensation when urinating
- Passing frequent, small amounts of urine
- Cloudy or strong-smelling urine
- Blood in the urine
- Pelvic pain (in women), especially in the center of the pelvis
- Fever and back pain (in cases of kidney infection)
If you notice any of these symptoms, especially if they are persistent or worsening, it’s important to seek medical attention.
How Are UTIs Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves:
- Urinalysis: A test of a urine sample to check for bacteria, white blood cells, or red blood cells.
- Urine culture: Identifies the specific bacteria causing the infection and helps guide antibiotic treatment.
- Imaging tests: Such as ultrasound or CT scans, may be recommended for recurrent infections or to check for structural abnormalities.
- Cystoscopy: In rare cases, a thin tube with a camera is inserted into the bladder for a closer look.
Treatment and Recovery
Most UTIs can be treated effectively with a short course of antibiotics. It’s essential to complete the full prescribed dose, even if symptoms improve, to ensure the infection is completely eliminated.
In addition to antibiotics, patients may be advised to:
- Drink plenty of water to help flush out bacteria
- Avoid caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods that can irritate the bladder
- Use a heating pad to ease pain or discomfort
For kidney infections or complicated cases, a longer course of treatment or hospitalization may be necessary.
Can UTIs Be Prevented?
Yes — there are several steps individuals can take to reduce their risk:
- Practice good personal hygiene
- Wipe from front to back after using the toilet
- Urinate after sexual activity
- Stay well-hydrated
- Avoid holding in urine for too long
- Wear breathable cotton underwear and avoid tight-fitting clothing
- Avoid using irritating feminine products in the genital area
For those who experience frequent UTIs, doctors may recommend preventive antibiotic therapy or other medical strategies.
UTIs in Men, Children, and the Elderly
While more common in women, UTIs can also occur in men, children, and older adults. In these groups, infections may present differently and carry a higher risk of complications, making proper diagnosis and treatment even more crucial.
Conclusion
Urinary Tract Infections are common, but they are also highly treatable and preventable. Recognizing the symptoms early and taking proactive steps to reduce risk can help keep your urinary system healthy. If UTIs become frequent or severe, consult a healthcare provider to explore underlying causes and long-term solutions.
The list of some Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) medicine:
Urobery
Cranbiotic