Antifungal medicines treat fungal infections. Fungus in the soil, air and on your skin can cause yeast infections, tinea, and nail and skin infections. Breathing in fungal spores can lead to respiratory sickness. People who have poorly immune systems are more prone to fungal infections that require antifungal medicine.
What are antifungals?
Antifungals are medicines that kill or stop the growth of fungi (the plural of fungus) that cause infections. They are also called antimycotic agents.
Fungal infections can affect the:
- Circulatory system.
- Respiratory system.
- Skin and nails.
What is a fungus?
Fungi grow as yeasts, molds or a combination of both. They reproduce through very tiny spores. These spores can exist in soil or become airborne.
You can also have naturally occurring fungi, like Candida yeast, in your body. Fungi live on your skin, inside your digestive system and vagina (part of the female reproductive system).
Who is at risk for fungal infections?
Anyone can get a fungal infection. Most fungi cause no problems or the infections are easily treatable.
People who have compromised immune systems are more likely to develop serious fungal infections. These infections are called opportunistic infections. They can be life-threatening for people who have:
- AIDS.
- Autoimmune diseases like lupus.
- Cancer.
- Organ transplants.
- Stem cell (bone marrow) transplants.
What do antifungals treat?
Antifungals treat these types of fungal skin infections:
- Athlete’s foot, jock itch and ringworm.
- Dandruff (seborrheic dermatitis).
- Fingernail infection or toenail fungus.
- Thrush and esophageal candidiasis (yeast infection in the mouth, throat or esophagus).
- Vaginitis and vaginal yeast infection.
Antifungals also treat more dangerous fungal infections like:
- Aspergillosis, pneumocystis pneumonia and Valley fever (lung infections).
- Candidemia (blood infection).
- Meningitis (brain infection).
- Ocular histoplasmosis syndrome (eye infection).
- Rhinosinusitis (sinus infection).
How do antifungal medications work?
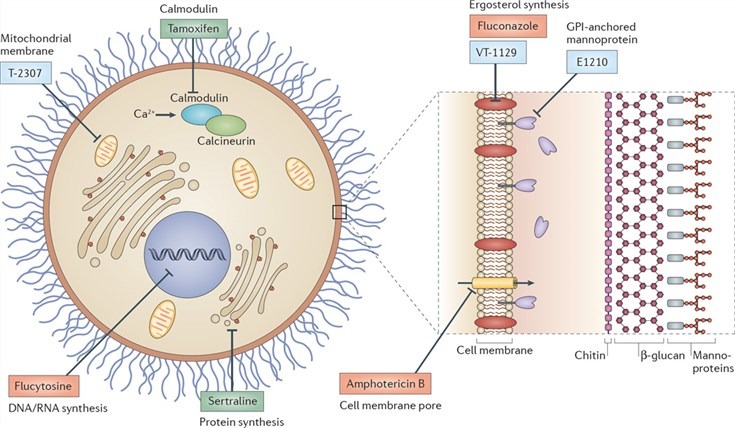
Antifungal medicines can kill a fungus. Or they may stop it from multiplying or growing. There are several classes of antifungal medications and different types of medicines. Your healthcare provider will select the best prescription medicine. Or they may guide you to an effective over-the-counter (OTC) treatment. Options include:
- Azoles (fluconazole or Diflucan®), synthetic (human-made) antifungals that keep fungi from growing.
- Echinocandins (micafungin or Mycamine®), newer semi-synthetic antifungals that attack and damage the fungus wall.
- Polyenes (nystatin or Bio-Statin®), organic (naturally occurring) antifungal treatments that destroy the fungus cell.
How do you take antifungal medications?
There are OTC and prescription antifungal medicines. Talk to your healthcare provider about what treatment to use.
Antifungals come in different forms, including:
- Injections (shots) or IV.
- Oral pills or liquids.
- Topical (skin) creams, ointments, gels and sprays.
- Vaginal suppositories.
How long do you need to take antifungal drugs?
Treatment length varies depending on the fungal infection. Some fungal skin infections like ringworm clear up in a few weeks. But it can take months or years to clear up some fungal nail, blood and lung infections.
What are the potential side effects of antifungals?
Side effects from antifungals vary. Results depend on the type of drug, dosage (strength) and fungus. You may experience:
- Abdominal pain, upset stomach and diarrhea.
- Itchy skin, burning sensation or skin rash.
Rarely, an antifungal drug may cause serious problems like:
- Liver damage (jaundice).
- Severe allergic reactions like anaphylaxis.
- Severe allergic skin reactions, such as blisters and peeling skin.
Who shouldn’t take antifungal medications?
Medication safety depends on the antifungal drug. Breastfeeding infants who develop thrush (an oral yeast infection) can get antifungal mouth drops. Their moms also need treatment, typically with an antifungal skin cream. Your healthcare provider can determine whether it’s OK for you or your child to take an antifungal medicine.
The list of some Antifungal medicine: