When we think of digestion, enzymes and stomach acids usually come to mind first. However, there’s another crucial player quietly working behind the scenes: bile acids. These remarkable molecules not only help digest fats but also play critical roles in regulating metabolism and maintaining gut health. Let’s dive deeper into the fascinating world of bile acids.
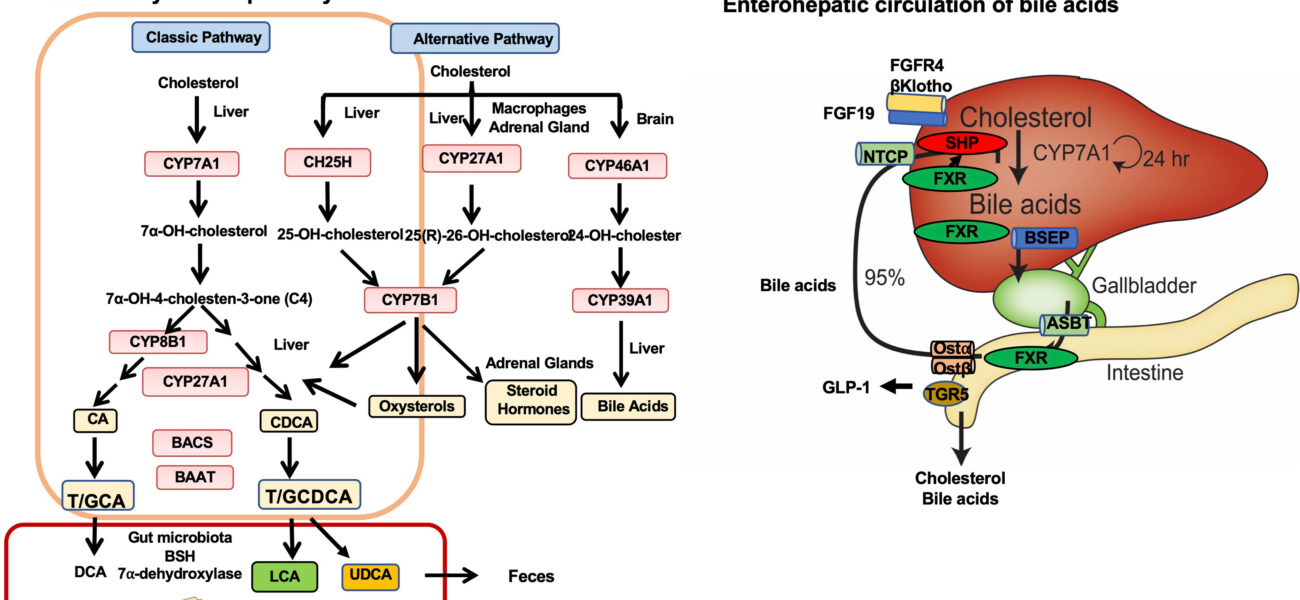
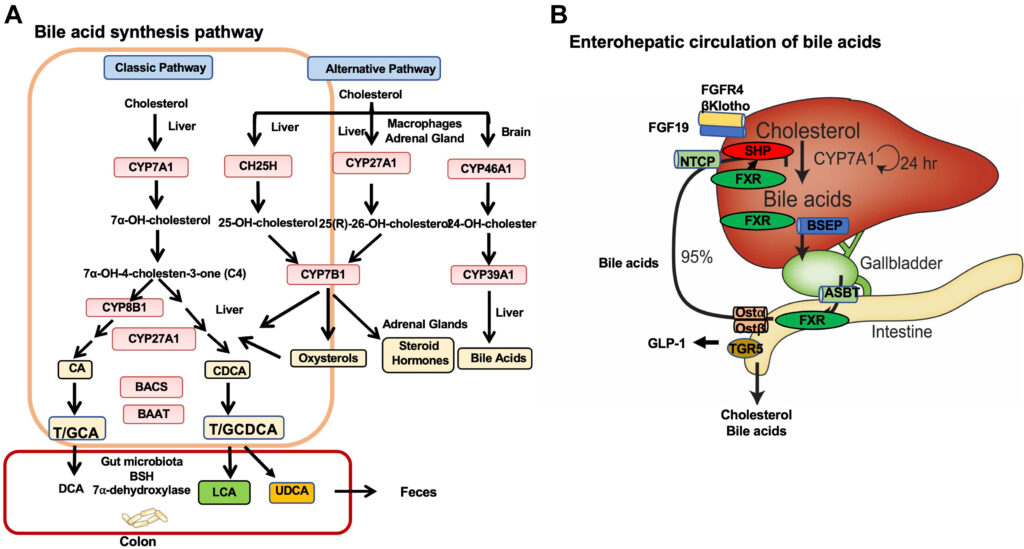
Bile acids are amphipathic molecules—meaning they have both water-loving and fat-loving parts—produced in the liver from cholesterol. Once synthesized, they are secreted into bile, stored in the gallbladder, and released into the small intestine when we eat, especially after meals rich in fat.
Their primary job is to break down fats into smaller droplets, making it easier for digestive enzymes (like lipase) to further break down the fats into fatty acids and glycerol for absorption.
Types of Bile Acids
There are two main categories:
- Primary bile acids: These are directly synthesized by the liver. The main ones in humans are cholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid.
- Secondary bile acids: These are formed when primary bile acids are modified by gut bacteria in the intestine. Examples include deoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid.
Together, these bile acids form a highly efficient system to manage fat digestion and absorption.
The Bile Acid Cycle
Bile acids are too valuable to waste, which is why the body recycles them through a process called the enterohepatic circulation. After aiding digestion in the intestines, most bile acids are reabsorbed into the bloodstream, returned to the liver, and reused. Only a small percentage are excreted in the feces, which is why the liver continuously makes just enough to replace the loss.
This recycling process not only conserves energy but also ensures that bile acids are available whenever needed for digestion.
Beyond Digestion: Other Important Functions
While fat digestion is their most famous role, bile acids have several other critical functions:
- Regulating metabolism: Bile acids act like hormones by binding to specific receptors, influencing the metabolism of fats, glucose, and energy.
- Maintaining gut health: They help control the composition of gut bacteria by creating an environment that favors beneficial microbes over harmful ones.
- Detoxification: Bile acids assist in the elimination of waste products, including excess cholesterol, drugs, and toxins from the body.
Recent research has also linked bile acid imbalances to diseases like diabetes, obesity, liver disorders, and even certain cancers.
Disorders Related to Bile Acids
Problems with bile acid production, secretion, or recycling can lead to various health issues:
- Cholestasis: A condition where bile flow is reduced or blocked, leading to a buildup of bile acids in the liver and bloodstream. It can cause jaundice, itching (pruritus), and liver damage.
- Gallstones: These often form when bile contains too much cholesterol and not enough bile acids to keep it dissolved.
- Bile acid malabsorption: This can cause chronic diarrhea and abdominal discomfort.
- Liver diseases: Conditions like primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) and primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) directly affect bile acid pathways.
Managing Bile Acid Health
Maintaining healthy bile acid production and flow is essential for overall well-being. Some ways to support this include:
- Healthy diet: A diet rich in fiber supports good gut bacteria that interact positively with bile acids.
- Staying hydrated: Adequate hydration assists in proper bile production and flow.
- Regular exercise: Physical activity can promote better liver function and bile metabolism.
- Medical management: In cases of bile acid-related diseases, medications like bile acid sequestrants or ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) may be prescribed.
Consulting a healthcare provider is crucial if you experience symptoms like persistent abdominal pain, unexplained itching, jaundice, or digestive issues.
Final Thoughts
Bile acids are much more than simple fat emulsifiers. They are dynamic, multifunctional molecules that are essential for digestion, metabolic health, and detoxification. As research continues to uncover their complex roles, it’s becoming clear that keeping bile acids in balance is key to maintaining overall health.
So the next time you enjoy a meal, remember—bile acids are working silently but powerfully to keep you healthy from the inside out.
The list of some Bile Acids medicine:
Olestar