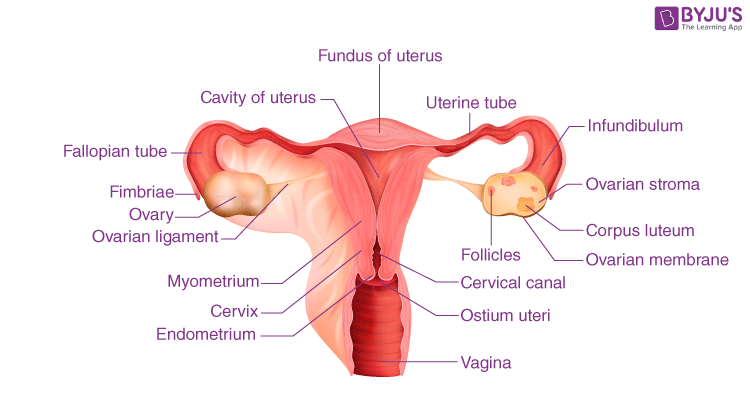
Fallopian tube cancer, also known as tubal cancer, progress in the fallopian tubes that connect the ovaries and the uterus. It is very infrequent and accounts for only 1 percent to 2 percent of all gynecologic cancers. About 1,500 to 2,000 cases of fallopian tube cancer have been information global. estimated 300 to 400 women are diagnosed with the condition annually in the United States.
It is more common for cancer to expanse, or metastasize, from other parts of the body, such as the ovaries or endometrium, than for cancer to actually create in the fallopian tubes.
Fallopian tube cancer ordinary affects women between the ages of 50 and 60, although it can happen at any age. It is more common in Caucasian women who have had small number or no children.
Because this cancer is so infrequent, little is known about what reason it. However, researchers are explore whether genetics play a role. There is evidence that women who have heir the gene linked to breast and ovarian cancer, called BRCA1, are also at an increased risk of developing fallopian tube cancer.
Symptoms
In its early stages, fallopian tube cancer often has no symptoms (asymptomatic), but is sometimes discovered during gynaecological tests for other agreement. Symptoms tend to happen once the cancer has reached its later stages, and could include:
• Watery or blood-stained vaginal emit
• Swelling of the lower abdomen that is not attached with weight gain
• A lump in the lower abdomen
• Pain in the lower abdomen
• A sensation of pressure against the bowel or reins
• The feeling that the bowel or reins can’t be fully emptied
• Unusual vaginal bleeding that’s not related with menstruation.
Causes
Doctors don’t know accurately why fallopian tube Cancer happens. You may have a superior chance of having it if you’ve:
• Never given birth
• Never breastfed a child
• Never used birth control pills
Having a close relative (mother, sister, daughter) with ovarian or breast cancer also increment your risk. You’re more likely to get fallopian tube cancer if you heir a change (mutation) to the BRCA gene, which makes ovarian and breast cancers more likely.
One theory is that long-lasting infections of the reproductive tract might trigger this cancer. But this hasn’t been proved.
Risk factors
- Factors that increase the chances of developing fallopian tube cancer include:
- Age (more than half of women who develop fallopian tube cancer or ovarian cancer are over 63).
- Changes (mutations) to the breast cancer (BRCA) gene.
- Early menstruation before age 12 or late menopause.
- Endometriosis.
- Ethnicity and origin (people living in North America or those of Northern European or Ashkenazi Jewish heritage are most at risk).
- Family history of breast cancer, ovarian cancer or fallopian tube cancer.
- Hormone replacement therapy after menopause.
- Infertility problems or having no pregnancies.
- Inherited conditions, such as Lynch syndrome and Peutz-Jeghers syndrome.
- Obesity (especially during early adulthood).
Treatment
Treatment rely on a number of different factors including the woman’s general health, whether or not she wants to have children, the size and stage of the cancer (whether it has expansion to other areas of the body).
Treatment may include:
Salpingo-oophorectomy – surgery to remove the ill fallopian tube and its ovary
Bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy – surgeryto remove both of the fallopian tubes and the ovaries
Hysterectomy – surgery to remove the internal reproductive organs, including fallopian tubes, ovaries and uterus
The omentum is removed (this is an apron of fat that hangs down from the stomach), and multiple biopsies (small samples of tissue) are usually taken to fully stage the cancer (check if there are any signs of spread of the cancer outside of the tube).
Bowel resection – surgery may be needed if the cancer has spread to include the bowel
Chemotherapy – the use of cancer-killing drugs, often in combination. Chemotherapy can be helpful in controlling secondary cancers because the whole body is treated. This is usually required for these cancers after surgery
Radiation therapy – the use of precisely targeted x-rays to kill cancer cells. This is not commonly used.
The list of some Fallopian tube cancer medicine: