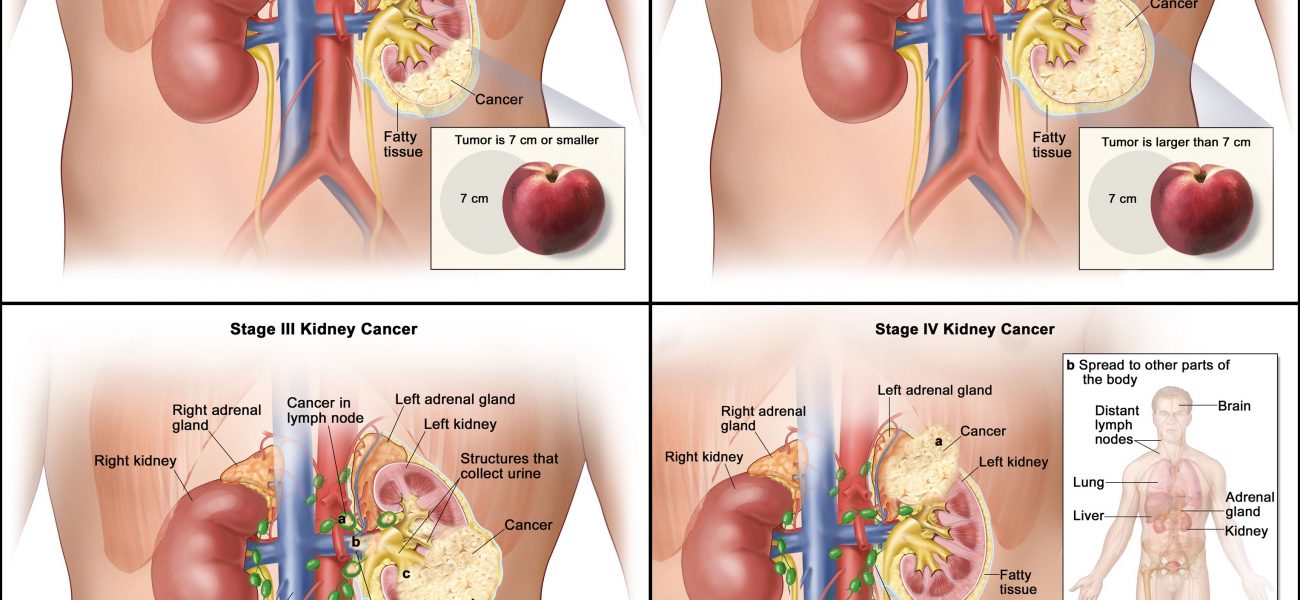
Kidney cancer — also called renal cancer — is a disease in which kidney cells become injurious (cancerous) and grow out of control, forming a tumor. Almost all kidney cancers first be manifest in the lining of tiny tubes (tubules) in the kidney. This type of kidney cancer is called renal cell carcinoma. The good news is that most kidney cancers are found before they spread (metastasize) to faraway organs. And cancers caught early are easier to treat successfully. However, these tumors can grow to be quite large before they are detected.
The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs, each about the size of a fist. They lie in your lower abdomen on each side of your spine. Their main job is to clean your blood, remove waste products, and make urine.
Doctors don’t know the causes of kidney cancer. But certain factors be manifest to increase the risk of getting kidney cancer. For example, kidney cancer occurs most often in people older than age 40. These are some other risk factors for kidney cancer Smoking. If you smoke cigarettes, your risk for kidney cancer is twice that of nonsmokers. Smoking cigars may also increase your risk.
- Being male. Men are about twice as likely as women to get kidney cancer.
- Being obese. Extra weight may cause changes to hormones that increase your risk.
- Using certain pain medications for a long time. This includes over-the-counter drugs in addition to prescription drugs.
- Having advanced kidney disease or being on long-term dialysis, a treatment for people with kidneys that have stopped working
- Having certain genetic conditions, such as von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) disease or inherited papillary renal cell carcinoma
- Having a family history of kidney cancer. The risk is especially high in siblings.
- Being exposed to certain chemicals, such as asbestos, cadmium, benzene, organic solvents, or certain herbicides
- Having high blood pressure. Doctors don’t know whether high blood pressure or medication used to treat it is the source of the increased risk.
- Being black. The risk in blacks is slightly higher than in whites. No one knows why.
- Having lymphoma. For an unknown reason, there is an increased risk of kidney cancer in patients with lymphoma.
Symptoms
Kidney cancer usually doesn’t have signs or symptoms in its early stages. In time, signs and symptoms may develop, including:
- Blood in your urine, which may appear pink, red or cola colored
- Pain in your back or side that doesn’t go away
- Loss of appetite
- Unexplained weight loss
- Tiredness
- Fever
Causes
It’s not clear what causes most kidney cancers.
Doctors know that kidney cancer begins when some kidney cells develop changes (mutations) in their DNA. A cell’s DNA contains the instructions that tell a cell what to do. The changes tell the cells to grow and divide rapidly. The accumulating abnormal cells form a tumor that can extend beyond the kidney. Some cells can break off and spread (metastasize) to distant parts of the body.
Risk factors
Factors that can increase the risk of kidney cancer include:
- Older age. Your risk of kidney cancer increases as you age.
- Smoking. Smokers have a greater risk of kidney cancer than nonsmokers do. The risk decreases after you quit.
- Obesity. People who are obese have a higher risk of kidney cancer than people who are considered to have a healthy weight.
- High blood pressure (hypertension). High blood pressure increases your risk of kidney cancer.
- Treatment for kidney failure. People who receive long-term dialysis to treat chronic kidney failure have a greater risk of developing kidney cancer.
- Certain inherited syndromes. People who are born with certain inherited syndromes may have an increased risk of kidney cancer, such as those who have von Hippel-Lindau disease, Birt-Hogg-Dube syndrome, tuberous sclerosis complex, hereditary papillary renal cell carcinoma or familial renal cancer.
- Family history of kidney cancer. The risk of kidney cancer is higher if close family members have had the disease.
Prevention
Taking steps to improve your health may help reduce your risk of kidney cancer. To reduce your risk, try to:
- Quit smoking. If you smoke, quit. Many options for quitting exist, including support programs, medications and nicotine replacement products. Tell your doctor you want to quit, and discuss your options together.
- Maintain a healthy weight. Work to maintain a healthy weight. If you’re overweight or obese, reduce the number of calories you consume each day and try to be physically active most days of the week. Ask your doctor about other healthy strategies to help you lose weight.
- Control high blood pressure. Ask your doctor to check your blood pressure at your next appointment. If your blood pressure is high, you can discuss options for lowering your numbers. Lifestyle measures such as exercise, weight loss and diet changes can help. Some people may need to add medications to lower their blood pressure. Discuss your options with your doctor.
The list of some Kidney cancer medicine: